A2Perf is a comprehensive benchmarking suite designed to bridge the gap between algorithms research and real-world applications for autonomous agents. This work addresses the critical need for benchmarks that incorporate practical metrics beyond raw task performance, enabling researchers to develop algorithms with real-world deployment considerations in mind.
Authors and Affiliations:
- Ikechukwu Uchendu - Google DeepMind & Harvard University
- Jason Jabbour - Harvard University
- Korneel Van den Berghe - Delft University of Technology
- Joel Runevic - Harvard University
- Matthew Stewart - Harvard University
- Jeffrey Ma - Harvard University
- Srivatsan Krishnan - Harvard University
- Izzeddin Gur - Google DeepMind
- Austin Huang - Google DeepMind
- Colton Bishop - Google DeepMind
- Paige Bailey - Google DeepMind
- Wenjie Jiang - Google DeepMind
- Ebrahim M. Songhori - Google DeepMind
- Sergio Guadarrama - Google DeepMind
- Jie Tan - Google DeepMind
- Jordan K. Terry - Farama Foundation
- Aleksandra Faust - Google DeepMind
- Vijay Janapa Reddi - Google DeepMind & Harvard University
Project Overview
Autonomous agents observe their environment, make decisions, and perform tasks with minimal human interference. While these agents have been successfully evaluated across a wide range of application domains, developing algorithms for autonomous agents that can be deployed in real-world scenarios presents significant challenges.
These challenges include dealing with high-dimensional state and action spaces, partial observability, non-stationarity, sparse rewards, and the need for safety constraints. Furthermore, real-world environments often have multiple objectives, require sample efficiency, and necessitate robust and explainable decision-making.
Key Contributions
A2Perf introduces several key innovations in benchmarking autonomous agents:
- Unified Evaluation Framework: Combines critical metrics spanning data cost, system resources, reliability, and generalization
- Real-World Domains: Three challenging domains with demonstrated real-world applicability
- Novel Data Cost Metric: Enables fair comparisons between different learning paradigms
- Open-Source Implementation: Extensible framework that facilitates reproducible evaluation
Three Real-World Domains
A2Perf incorporates three challenging domains that closely mirror scenarios demonstrated in the real world:

Figure 1: The three domains included in A2Perf: computer chip floorplanning for optimizing integrated circuit layouts, web navigation for automated form filling and website interaction, and quadruped locomotion for robotic control.
1. Computer Chip Floorplanning
This domain was used to help create an iteration of Google's Tensor Processing Unit, where the agent optimizes the layout of chip components. The computer chip-floorplanning domain exhibits a small Sim2Real gap, making it highly relevant for real-world applications in semiconductor design.
2. Web Navigation
Agents autonomously navigate and interact with websites in a Google Chrome browser, making it identical to real-world web navigation. This domain includes form-filling and website interaction tasks that are commonly performed in industrial and consumer contexts.
3. Quadruped Locomotion
This domain has demonstrated successful transfer of learned walking gaits to the Unitree Laikago robot. The quadruped locomotion domain represents a critical application area for autonomous robotics with clear real-world implications.
Comprehensive Metrics Framework
A2Perf provides an open-source benchmarking suite that evaluates agents across four key metric categories:
1. Data Cost
Quantifies the effort required to gather training data for imitation learning, enabling fair comparisons between different learning paradigms (e.g., imitation learning vs reinforcement learning).
2. Application Performance
Relates to the quality of the agent's task-specific execution and its ability to generalize to tasks that it was not explicitly trained to perform.
3. System Resource Efficiency
Focuses on the hardware resources used during training and inference, including compute requirements, wall-clock time, and memory usage.
4. Reliability
Denotes the consistency of an agent's performance over training and inference, which is crucial for real-world deployment scenarios.
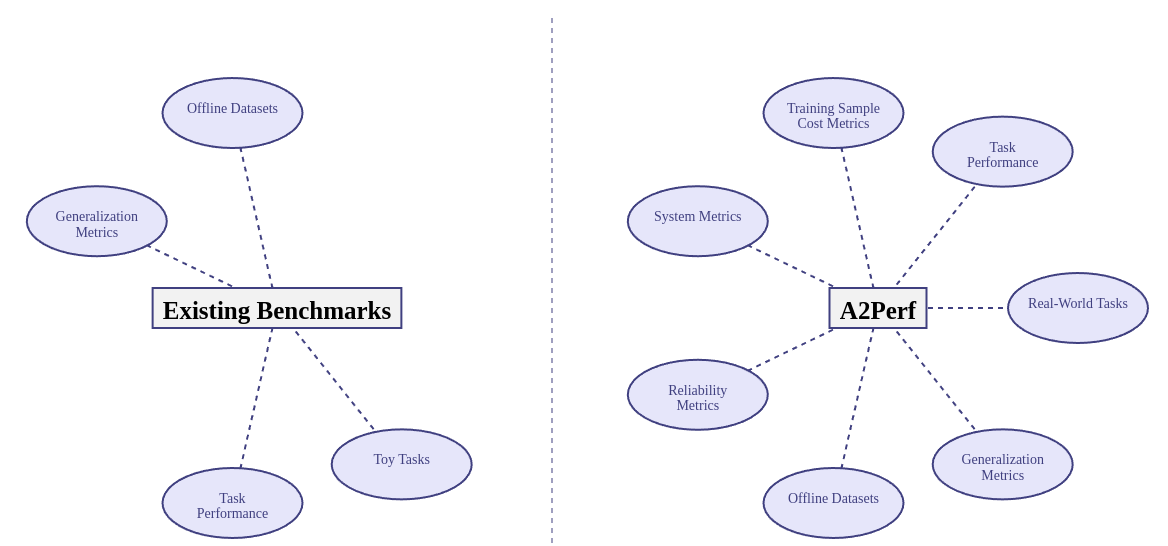
Figure 2: A2Perf compared to existing benchmarks that evaluate autonomous agents. A2Perf distinguishes itself by including metrics for generalization, system resource efficiency, data cost, and reliability.
Experimental Insights
Our experimental evaluation yields valuable insights into the real-world applicability of autonomous agents across diverse domains:
Web Navigation Performance
In the web navigation domain, we explore the feasibility of deploying agents by analyzing their inference time, power usage, and memory consumption. The results demonstrate that trained agents can operate with latencies comparable to human reaction times on consumer-grade hardware.
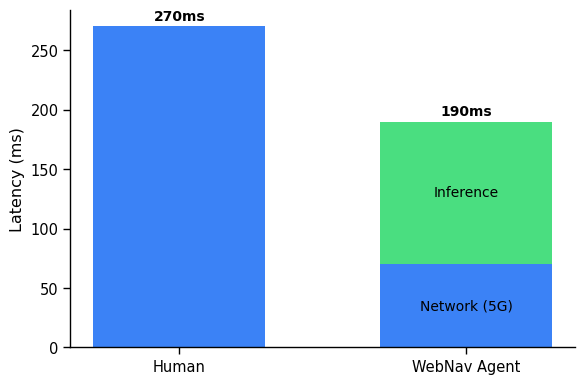
Figure 3: Comparison between human and web navigation agent performance, showing that trained agents can achieve latencies comparable to human reaction times.
Reliability in Chip Floorplanning
For chip floorplanning, we find that the PPO algorithm provides more consistent initial placements compared to DDQN, reducing variability for designers. This highlights the importance of considering reliability metrics in real-world applications.
Quadruped Locomotion Stability
In quadruped locomotion, PPO exhibits superior stability during training, while SAC demonstrates more consistent gaits during deployment. These findings underscore the importance of considering reliability in real-world scenarios.
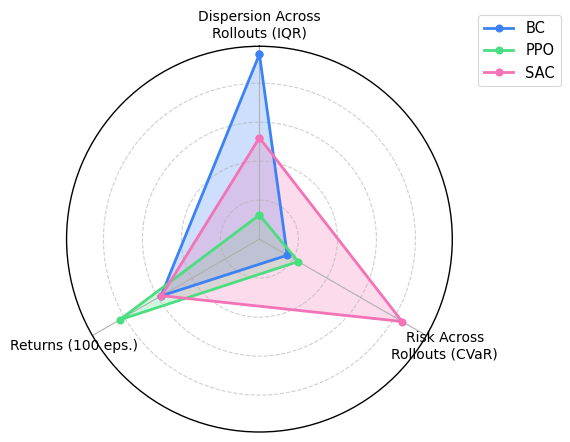
Figure 4: Reliability analysis for quadruped locomotion, showing the consistency of different algorithms during deployment.
Impact and Significance
A2Perf represents a significant step forward in benchmarking autonomous agents for real-world applications. By providing a comprehensive evaluation framework that goes beyond raw task performance, A2Perf enables researchers to develop algorithms with practical deployment considerations in mind.
The benchmark's focus on real-world domains with demonstrated transfer capabilities ensures that the results are relevant and applicable to practical applications. The inclusion of novel metrics such as data cost and reliability provides insights that are crucial for successful real-world deployment.
As an open-source and extensible benchmark, A2Perf is designed to remain accessible, documented, up-to-date, and useful to the research community over the long term. The framework allows for straightforward expansion to benchmark on custom domains and for custom metrics, making it a valuable tool for the broader autonomous systems research community.
Code and Resources
The A2Perf implementation is available as open-source software: https://github.com/Farama-Foundation/A2Perf
For more information about the Farama Foundation and their mission to advance reinforcement learning research, visit: https://farama.org